GDPR Compliance in Marketing
Introduction
In the digital era, data privacy is a major concern for consumers and a regulatory priority. The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), effective since 2018, has set high global data protection standards. For marketers, GDPR compliance is crucial not only legally but also as a strategic move to gain consumer trust and stay competitive. This blog delves into GDPR compliance, its significance for marketing, related regulations, and strategies for aligning marketing with current data privacy trends.
GDPR mandates that organizations processing EU residents’ personal data ensure privacy and obtain explicit consent. For marketers, this means strict data handling and transparency requirements, making data protection a strategic asset that enhances consumer trust. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, such as Amazon’s €746 million fine in 2022. Embracing GDPR principles is now essential to thrive in today’s privacy-conscious market.
Understanding GDPR and Global Privacy Regulations
The GDPR is founded on several key principles that guide the processing and protection of personal data, here are a few of the principles:
- Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency: Data must be processed legally, fairly, and transparently, with clear communication to individuals about how their data is being used.
- Purpose Limitation: Personal data should be collected for specified, legitimate purposes and not processed in a manner incompatible with those purposes.
- Integrity and Confidentiality: Appropriate technical and organizational measures must be implemented to ensure the security of personal data, protecting it against unauthorized or unlawful processing, accidental loss, destruction, or damage.
The GDPR grants individuals several rights regarding their personal data. Two key Rights are the Right of Access, which allows individuals to access their personal data held by an organization and obtain information about its processing, and the Right to Erasure (Right to be Forgotten), enabling individuals to request the deletion of their personal data under certain circumstances, such as when the data is no longer necessary for its original purpose.
Additional rights include the Right to Rectification, Right to Restriction of Processing, Right to Data Portability and Right to Object.
Global Privacy Regulations
While the GDPR sets a comprehensive framework for data protection within the EU, various other regions and countries have implemented their own privacy regulations to safeguard the rights of individuals. Understanding and complying with these diverse regulations is crucial for businesses operating globally. Some notable examples include:
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): The CCPA has a broader scope, applying to businesses that meet certain criteria, regardless of their physical location.
- LGPD (Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados – Brazil): Similar to GDPR, the LGPD emphasizes consent, data processing requirements, and the rights of data subjects, such as access, rectification, and deletion of personal data.
- Other Regional Regulations: Countries like Canada (PIPEDA), Japan (APPI), and Australia (Privacy Act) have their own privacy laws and regulations.
As data flows transcend borders, businesses must stay informed and compliant with the diverse and evolving privacy laws in the regions where they operate or serve customers. Navigating this complex web of global privacy regulations presents a significant challenge for marketers, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive, privacy-first approach to data handling and marketing practices.
The Digital Markets Act (DMA)
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) is a landmark legislation introduced by the European Union to promote fair competition in digital markets by regulating the practices of large online platforms, known as “gatekeepers.” This is a regulation taking effect in early 2024, which is a good example of the constantly changing regulatory environment, which makes it important to regularly review the privacy policies and practices and to continuously be up-to-date with any upcoming changes, or new policies.
By proactively addressing the DMA’s requirements, marketers can navigate the evolving regulatory landscape while maintaining a consumer-centric approach to data privacy and advertising practices.
The Phase-Out of Third-Party Cookies Background
In recent years, concerns over user privacy and data protection have led to significant shifts in the digital advertising landscape. One of the most notable changes is Google’s decision to phase out third-party cookies by the end of 2024.
Implications for Marketing The phase-out of third-party cookies presents both challenges and opportunities for marketers:
- Challenges:
- Loss of Cross-Site Tracking: Without third-party cookies, marketers will lose the ability to track user behavior across different websites, making it harder to build comprehensive user profiles and target ads based on browsing history.
- Disruption to Existing Strategies: Many marketing strategies and platforms have been built around the use of third-party cookies, and their removal will require significant adjustments and the adoption of new techniques.
- Opportunities:
- Focus on First-Party Data: The phase-out of third-party cookies presents an opportunity for marketers to shift their focus towards collecting and leveraging first-party data, which is data collected directly from users through their interactions with a brand’s owned channels (e.g., website, apps, newsletters).
- Privacy-First Marketing: By embracing privacy-first marketing strategies, brands can build trust with consumers and differentiate themselves in an increasingly privacy-conscious market.
By adapting to the phase-out of third-party cookies and embracing privacy-first marketing strategies, brands can stay ahead of the curve and maintain effective marketing practices while respecting consumer privacy.
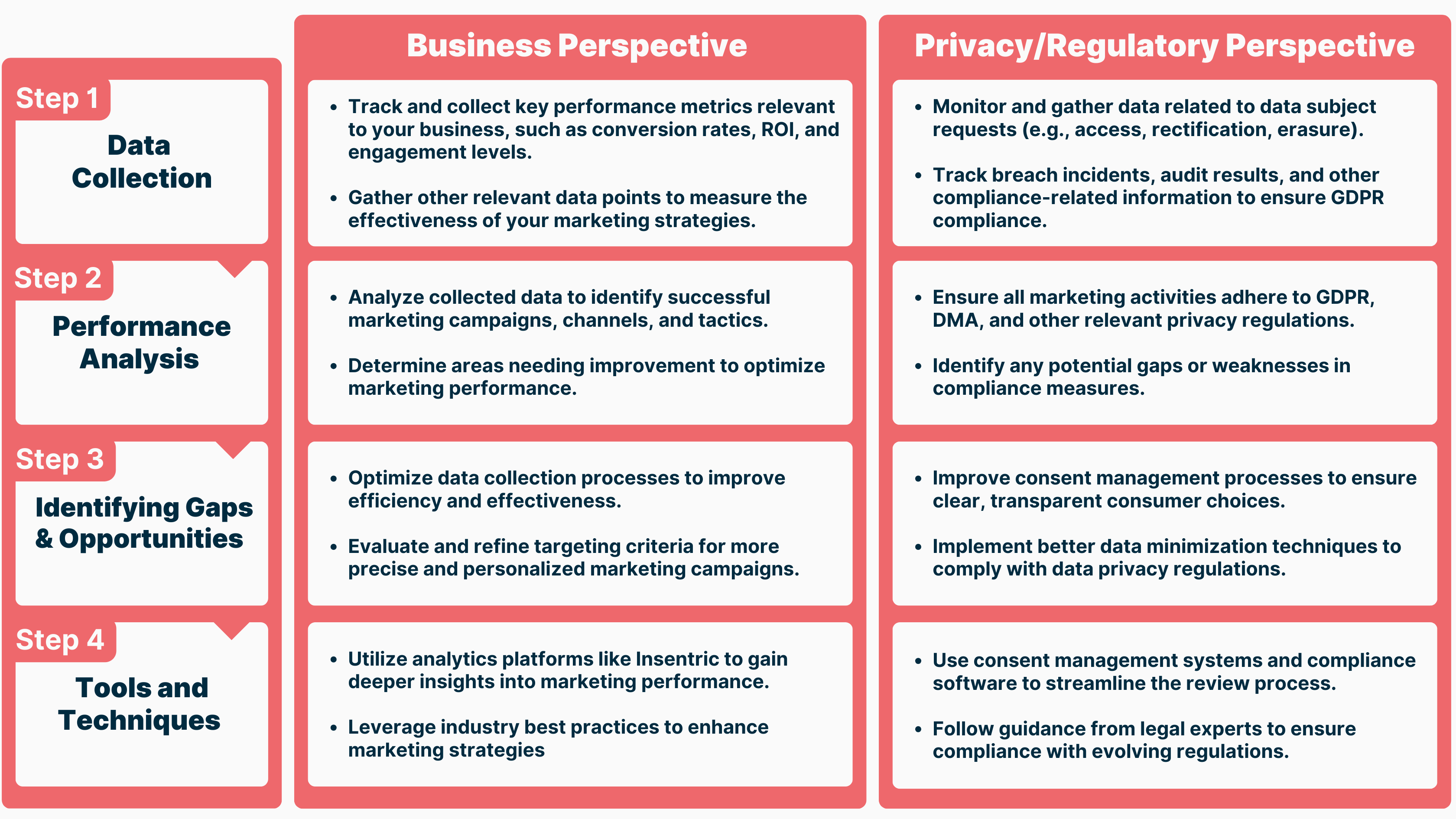
Conducting a systematic Marketing Review
The Importance of Systematic Reviews in the ever-changing landscape of data privacy regulations and consumer expectations, conducting regular marketing reviews is essential for ensuring compliance, identifying performance issues, and adapting strategies to market changes. These reviews provide a critical opportunity to assess the effectiveness of current marketing practices, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments to align with evolving regulatory requirements and consumer preferences.
Step-by-Step Guide To conduct a comprehensive marketing review, follow these steps:
Conclusion
In the rapidly evolving landscape of data privacy regulations and consumer expectations, GDPR compliance, the Digital Markets Act, and the phase-out of third-party cookies are critical considerations for marketers. Regular reviews and strategic adjustments are essential to stay compliant, build consumer trust, and maintain effective marketing practices.
By understanding and proactively addressing these complexities, marketers can not only avoid legal pitfalls but also differentiate themselves as responsible, consumer-centric brands. Embracing data privacy as a strategic advantage and aligning marketing efforts with evolving regulations will foster long-term success in the digital age.
